
In this post, I will explain how to create GitOps platform with ArgoCD, GitHub and DockerHub step by step. There are so many kinds of source code repositories and container registries, but I chose GitHub and DockerHub. Because they are de-facto tools and they has free plan, so everyone can build GitOps platform.
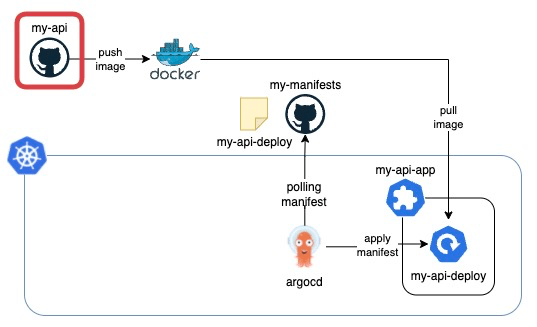
In this architecture, we utilize two GitHub repositories: one for storing manifests, and the other for application code. Furthermore, we leverage GitHub Actions to automate the process of building and pushing images to DockerHub. ArgoCD plays a crucial role in synchronizing the state of manifests with the corresponding Kubernetes applications!🐙
- Preparation
- Create Application in ArgoCD
- Fork GitHub repository
- Push image to DockerHub
- Deploy application!
- Practice GitOps – release new application –
- Wrap up
Preparation
- GitHub account
- GitHub repository for manifests [1]
- DockerHub account
- kubernetes[2]
- ArgoCD[2]
- ArgoCD Application that maintains ArgoCD Applications by following App of Apps pattern.[3]
[1] Please refer to my previous post and create a GitHub repository for manifests.
[2] Here are my versions of each tool for reference.
$ minikube profile list
|----------|-----------|---------|--------------|------|---------|---------|-------|--------|
| Profile | VM Driver | Runtime | IP | Port | Version | Status | Nodes | Active |
|----------|-----------|---------|--------------|------|---------|---------|-------|--------|
| minikube | docker | docker | 192.168.49.2 | 8443 | v1.26.3 | Running | 1 | * |
|----------|-----------|---------|--------------|------|---------|---------|-------|--------|
$ argocd version --short | grep argocd-server
argocd-server: v2.7.4+a33baa3.dirty
[3]If you’re not familiar with App of Apps pattern, please check the ArgoCD document or my previous post.
Create Application in ArgoCD
Let’s create Application called my-api-app with App of Apps pattern approach by adding a new manifest at GitHub repository for manifests called my-manifests. We will deploy our new pod in the Application later.
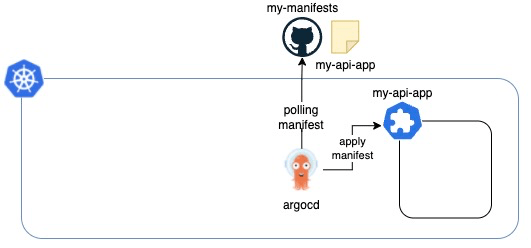
Create a manifest for Application
Store the following in a file called my-api-app.yaml, and put it under argocd-resources/applications/applications directory. Please put your repository’s URL in the repoURL field.
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: my-api-app
spec:
destination:
namespace: default
server: 'https://kubernetes.default.svc'
source:
path: my-api-app
repoURL: '<YOUR REPOSITORY URL>'
targetRevision: HEAD
sources: []
project: default
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: false
selfHeal: false
Reference: my file’s location
ls -la argocd-resources/applications/my-api-app.yaml
-rw-r--r-- 1 yukinakamura staff 391 Jul 1 15:55 argocd-resources/applications/my-api-app.yaml
Push the manifest to the GitHub repository
Commit and Push the manifest to the repository.
git add argocd-resources/applications/my-api-app.yaml \
&& git commit -m "Add my-api-app" \
&& git push
Check Application with ArgoCD
Please sign in your ArgoCD and check if Application called my-api-app has been created in Application called argocd-resources. (If you haven’t created Application called argocd-resources, Please refer to my previous post and create it.)

Please check if my-api-app has been created.

There is a error that says ‘rpc error: code = Unknown desc = my-api-app: app path does not exist’, but it is expected. In a later step, creating a manifest in my-api-app directory will resolve this error.

Now ArgoCD is ready, let’s go ahead and build a simple application!
Fork GitHub repository
Let’s create a repository for a simple application’s code. To save time, this procedure will create a new repository by forking my repository called my-api.
Access my-api and click Fork.
Click Create fork. After that, please check my-api repository has been created in your GitHub account.

Push image to DockerHub
Next, build and push an image to your DockerHub with GitHub Actions. I already have prepared a GitHub Actions script in my-api, so let’s use it.

Create DockerHub repository
Access DockerHub and click Create repository.

Create repository with Visibility as Public so that ArgoCD can access it without authentication. Here are my settings.
- Repository Name: my-api
- Description: application for kubernetes and argocd
- Visibility: Public

Set DockerHub credentials and repository name in GitHub Actions Secrets
My GitHub Actions script uses the following three GitHub Actions Secrets. So, please create them on your GitHub Repository’s Actions Secret.
- DOCKER_USERNAME : DockerHub username
- DOCKER_PASSWORD : DockerHub password
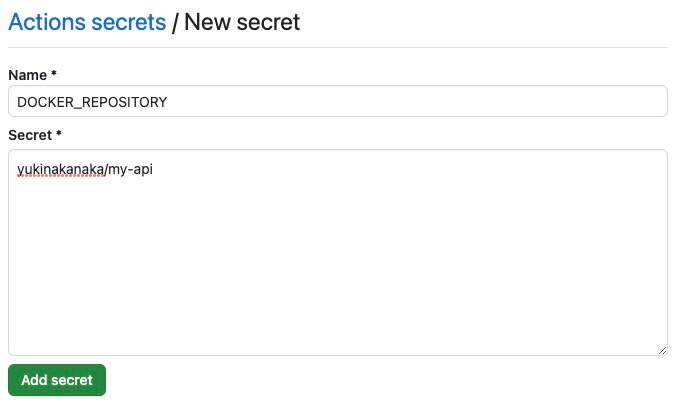
- DOCKER_REPOSITORY : DockerHub repository name
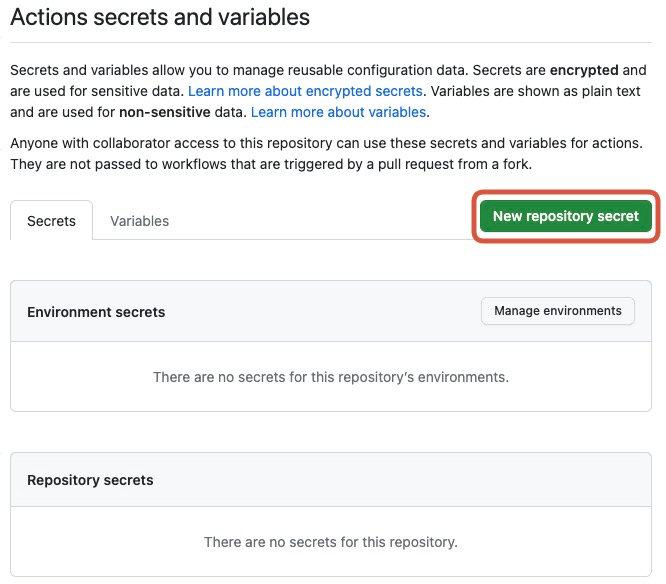
Access ‘Settings>Actions’.

Please create three secrets that I mentioned above. You can create a secret by clicking New repository secret.
Now we’re ready to push an image to DokcerHub!
Enable GitHub Actions
In the forked repository, GitHub Actions are disabled, so please enable them.
Access Actions tab and Click I understand my workflows, go ahead and enable them.

Push image to DockerHub repository
My GitHub Actions script build image and push it to DockerHub repository automatically, when you create a release on GitHub. So, let’s create a release now!
Access your GitHub repository and click Create a new release.

Create a tag
Click Choose a tag, then put v0.0.1 in the form and click Create a new tag. This tag will be a docker image’s tag.

Publish release
Fill the form and Click Publish release. Any title and description are fine. Here are my settings.
- Title: Release v0.0.1
- Description: Release v0.0.1!

Check GitHub Actions result and DockerHub
Access Actions tab, then check if workflow run successfully.

Access your DockerHub repository, then check if there is v0.0.1 tag.

Now that the Docker image is ready, let’s Deploy it using ArgoCD!
Deploy application!

Create a manifest of Deployment
Let’s create a manifest of Deployment in my-manifests repository.
Please created my-api-app directory at the top directory of my-manifests.
cd my-manifests
mkdir my-api-app && cd my-api-app
Store the following in a file called my-api-deploy.yaml, and put it under my-api-app directory. Please put your DockerHub Repository name in the image field.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: my-api
name: my-api
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: my-api
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: my-api
spec:
containers:
- image: <YOUR DOCKERHUB REPOSITORY NAME>:v0.0.1
name: my-api
resources:
requests:
cpu: 200m
memory: 200Mi
limits:
cpu: 200m
memory: 200Mi
Commit and Push to manifests repository
git add my-api-deploy.yaml \
&& git commit -m “Add my-api-deploy” \
&& git push
Check ArgoCD
Access ArgoCD and check my-api-app. You can see a pod is running!
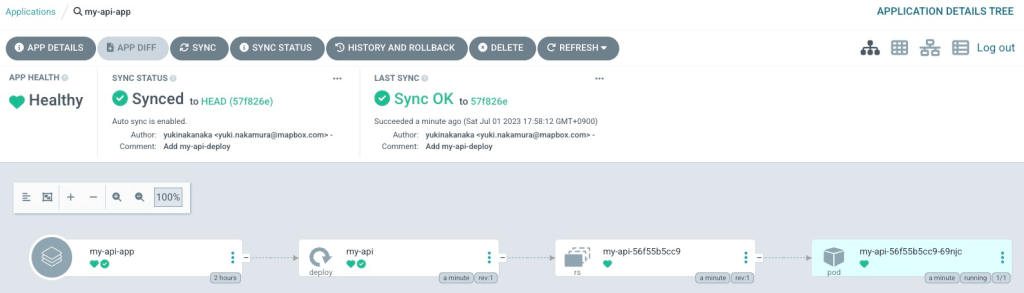
If you cannot see any pod is running, please click REFRESH.

Now we have GitOps platform, so let’s practice GitOps!
Practice GitOps – release new application –
Edit application’s source code
Please edit some parts of application’s source code. For example, edit the 8th line of my-api/app/main.py.
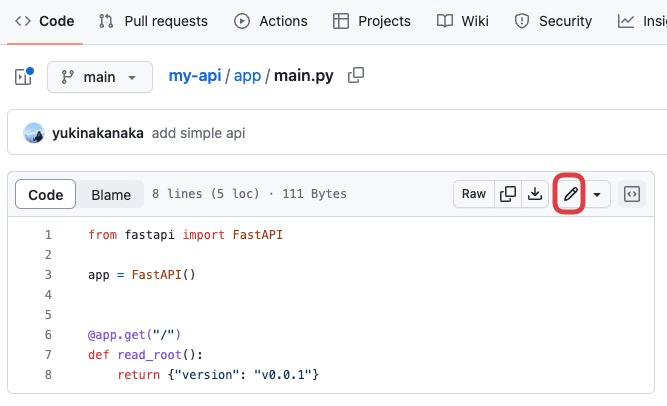
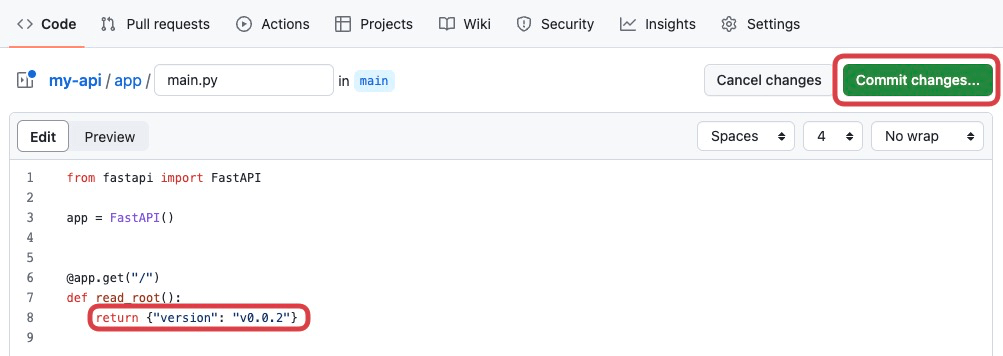
Commit changes
Create a new image
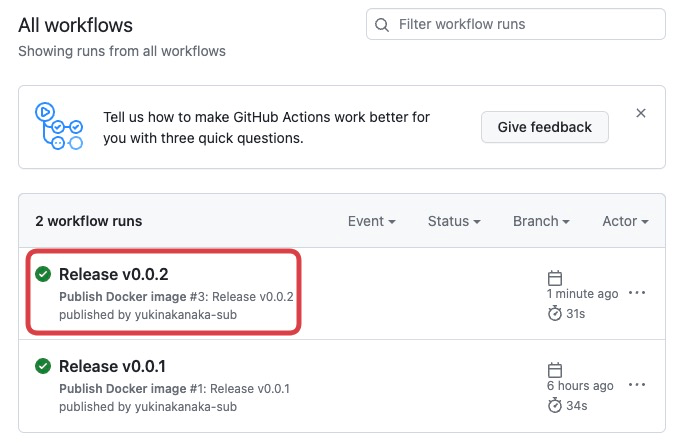
Create a new image with GitHub Action by creating a new release on GitHub.

Publish release.

Access GitHub Actions and DockerHub, and check if a new image has been created.

Deploy v0.0.2 image
Edit image’s tag on my-api-deployment.yaml and Commit. Then, Then ArgoCD should detect the change in manifest and automatically deploy the new image!

Please check if the new image has been deployed on ArgoCD.

Wrap up
We created GitOps platform with ArgoCD, GitHub and DockerHub. Finally, we deployed a new image with GitOps approach!
Thank you for reading! 🐙

