
Event-driven workflow in Kubernetes
Argo Events is an event-driven workflow automation framework for Kubernetes which helps you trigger K8s objects, Argo Workflows, Serverless workloads, etc. With Argo Events, we can trigger workflow such as CI/CD pipeline and ETL pipeline using some kinds of events sources. In this article, I will explain how to install Argo Events via Helm and how to create a simple event-driven workflow.
- Preparation
- Add argo’s chart repository
- Create a simple event-driven workflow with Argo Events
- (Optional) Manage Argo Events via ArgoCD
- Wrap up
Preparation
Please install tools below.
Required
- kubernetes[1]
- Helm[1]
[1] Here are my versions of each tool.
$ minikube profile list
|----------|-----------|---------|--------------|------|---------|---------|-------|--------|
| Profile | VM Driver | Runtime | IP | Port | Version | Status | Nodes | Active |
|----------|-----------|---------|--------------|------|---------|---------|-------|--------|
| minikube | docker | docker | 192.168.49.2 | 8443 | v1.26.3 | Running | 1 | * |
|----------|-----------|---------|--------------|------|---------|---------|-------|--------|
$ helm version
version.BuildInfo{Version:"v3.12.0", GitCommit:"c9f554d75773799f72ceef38c51210f1842a1dea", GitTreeState:"clean", GoVersion:"go1.20.4"}
Optional
If you’d like to install Argo Events with GitOps way, please prepare below, too.
- ArgoCD[2]
- GitHub repository for manifests
- Please refer to my previous post and create a GitHub repository for manifests.
- ArgoCD Application that maintains ArgoCD Applications by following App of Apps pattern.
- If you’re not familiar with App of Apps pattern, please check the ArgoCD document or my previous post.
[2] Here are my ArgoCD version.
$ argocd version --short | grep argocd-server
argocd-server: v2.7.4+a33baa3.dirty
Add argo’s chart repository
ArgoCD’s Helm Charts are maintained on argoproj/argo-helm. Also, they are hosted at https://argoproj.github.io/argo-helm/ . Let’s add it to your helm.
helm repo add argo https://argoproj.github.io/argo-helm
If you’ve already added it, please update it.
helm repo update argo
There are several charts in the repository. You can find argo-events’ chart by the following command.
helm search repo argo | grep argo-events
example:
helm search repo argo | grep argo-events
argo/argo-events 2.4.0 v1.8.0 A Helm chart for Argo Events, the event-driven ...
Check available charts’ versions and Argo Event’s versions
You can check available versions via helm search with –versions option.
helm search repo argo/argo-events --versions | head -5
example:
NAME CHART VERSION APP VERSION DESCRIPTION
argo/argo-events 2.4.0 v1.8.0 A Helm chart for Argo Events, the event-driven ...
argo/argo-events 2.3.3 v1.7.6 A Helm chart for Argo Events, the event-driven ...
argo/argo-events 2.3.2 v1.7.6 A Helm chart for Argo Events, the event-driven ...
argo/argo-events 2.3.1 v1.7.6 A Helm chart for Argo Events, the event-driven ...
This time, I chose the latest Chart version (2.4.0) of Chart that uses v1.8.0 Argo Events App.
Run helm install
Install Argo Events by helm install !
helm install argo-events argo/argo-events -n argo-events --create-namespace --version 2.4.0
Check resources of Argo Events
You can know Architecture of Argo Events in details here. Argo Events has many k8s’ objects. Let’s take a look at them.
Namespaced resources
kubectl get -A -l helm.sh/chart=argo-events-2.4.0 \
"$(kubectl api-resources --namespaced=true --verbs=list -o name | tr "\n" "," | sed -e 's/,$//')"
NAMESPACE NAME DATA AGE
argo-events configmap/my-argo-events-controller-manager 1 4m42s
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
argo-events pod/my-argo-events-controller-manager-787d58f964-t8krc 1/1 Running 0 4m42s
NAMESPACE NAME SECRETS AGE
argo-events serviceaccount/my-argo-events-controller-manager 0 4m42s
argo-events serviceaccount/my-argo-events-events-webhook 0 4m42s
NAMESPACE NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
argo-events deployment.apps/my-argo-events-controller-manager 1/1 1 1 4m42s
NAMESPACE NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
argo-events replicaset.apps/my-argo-events-controller-manager-787d58f964 1 1 1 4m42s
Non-namespaced resources
kubectl get -A -l helm.sh/chart=argo-events-2.4.0 \
"$(kubectl api-resources --namespaced=false --verbs=list -o name | tr "\n" "," | sed -e 's/,$//')"
NAME ROLE AGE
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/my-argo-events-controller-manager ClusterRole/my-argo-events-controller-manager 14m
NAME CREATED AT
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/my-argo-events-controller-manager 2023-08-05T06:42:45Z
CustomResourceDefinitions
kubectl get customresourcedefinitions.apiextensions.k8s.io
NAME CREATED AT
eventbus.argoproj.io 2023-08-05T06:42:45Z
eventsources.argoproj.io 2023-08-05T06:42:45Z
sensors.argoproj.io 2023-08-05T06:42:45Z
...
Create a simple event-driven workflow with Argo Events

Now, we’re ready to use Argo Events. So, let’s create a workflow with Argo Events! You can see all manifests of the application in my GitHub repo.
In the application, we will use a calendar as an Event Source to trigger a K8S job that writes event data to its log. Argo Events supports many Event Sources and Trigger Types, but I chose the calendar option this time because we don’t have to set up any other tools!
Create a namespace
Let’s create a namespace named argo-events-lab.
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: argo-events-lab
EOF
Create an Event Bus
EventBus is a Kubernetes Custom Resource which is used for event transmission from EventSources to Sensors. The common practice is to create an EventBus named default in the namespace. So, let’s create it. I chose Jetstream event bus, because it is the latest streaming server implemented by the NATS community.
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: EventBus
metadata:
name: default
spec:
jetstream:
version: latest
EOF
Please check the statefulset has been created.
kubectl get statefulset -l eventbus-name=default \
-n argo-events-lab
NAME READY AGE
eventbus-default-js 3/3 53s
Create an Event Source
Let’s create an Event Source that type is Calendar. Calendar has some scheduling patterns. This time, I chose the interval pattern.
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: EventSource
metadata:
name: calendar-event-source
namespace: argo-events-lab
spec:
calendar:
calendar-interval:
# creates an event every 60 seconds
interval: 60s
EOF
Please check the deployment has been created.
kubectl get deployment -l eventsource-name=calendar-event-source \
-n argo-events-lab
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
calendar-event-source-eventsource-6rzqx 1/1 1 1 6s
Create a Sensor
Let’s create a Sensor that uses Kubernetes Object Trigger. This time, we will create K8S job. The sensor will create jobs using event data. That configuration is defined in the parameters section.
*We need to create a ServiceAccount, Role and RoleBindings so that the sensor can create jobs.
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: calendar-sensor-sa
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: calendar-sensor-role
rules:
- apiGroups: ["batch", "extensions"]
resources: ["jobs"]
verbs: ["create"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: calendar-sensor-binding
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: calendar-sensor-role
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: calendar-sensor-sa
namespace: argo-events-lab
---
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Sensor
metadata:
name: calendar-sensor
namespace: argo-events-lab
spec:
template:
serviceAccountName: calendar-sensor-sa
dependencies:
- name: calendar-dep
eventSourceName: calendar-event-source
eventName: calendar-interval
triggers:
- template:
name: calendar-job-trigger
k8s:
operation: create
source:
resource:
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
generateName: calendar-job-
spec:
ttlSecondsAfterFinished: 120
template:
spec:
restartPolicy: Never
containers:
- image: busybox
name: echo-job
command: [echo]
args:
- "THIS_WILL_BE_REPLACED"
parameters:
- src:
dependencyName: calendar-dep
dest: spec.template.spec.containers.0.args.0
EOF
Please check the deployment has been created.
kubectl get deploy -l sensor-name=calendar-sensor \
-n argo-events-lab
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
calendar-sensor-sensor-8rjkz 1/1 1 1 22s
Check if the application is working
Let’s check if jobs are being created.
kubectl get job -l events.argoproj.io/sensor=calendar-sensor \
-n argo-events-lab
NAME COMPLETIONS DURATION AGE
calendar-job-9qvwn 1/1 7s 14s
Check the pod’s log. You can see the event’s context and data!
kubectl logs <YOUR JOB'S POD NAME> -n argo-events-lab | jq .
kubectl logs calendar-job-dx6zb-scv2q -n argo-events-lab | jq .
{
"context": {
"id": "62346462396534332d353363312d343438662d613566662d323362316563393131363430",
"source": "calendar-event-source",
"specversion": "1.0",
"type": "calendar",
"datacontenttype": "application/json",
"subject": "calendar-interval",
"time": "2023-08-05T15:00:03Z"
},
"data": "eyJldmVudFRpbWUiOiIyMDIzLTA4LTA1IDE1OjAwOjAyLjk5OTcxOTI5OSArMDAwMCBVVEMgbT0rMTc5LjQ4MzE2NTEyNCJ9"
}
(Optional) Manage Argo Events via ArgoCD
If you’re managing kubernetes add-on using App of Apps pattern of ArgoCD, please do followings.
Create Application manifest of Argo Events
Store the following in a file called my-argo-events.yaml.
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: my-argo-events
spec:
destination:
name: ''
namespace: argo-events
server: 'https://kubernetes.default.svc'
source:
path: ''
repoURL: 'https://argoproj.github.io/argo-helm'
targetRevision: 2.4.0
chart: argo-events
sources: []
project: default
syncPolicy:
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true
automated:
prune: false
selfHeal: false
I added a option, CreateNamespace=true, to create a new namespace named argo-events. The option is from Helm Install not ArgoCD.
Push the manifests to manifests repository
git add my-argo-events.yaml \
&& git commit -m "Add Application manifest of Argo Events" \
&& git push
Here is my commit on GitHub.
Check if it has been installed on ArgoCD UI.
Please sign in your ArgoCD UI, then check if Argo Events has been installed.
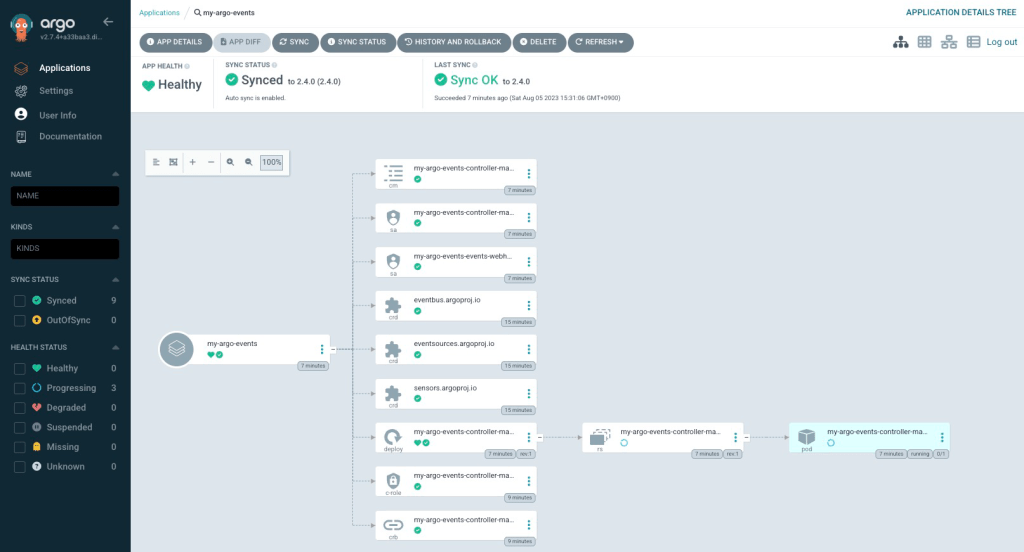
Wrap up
We installed Argo Events via Helm. Then, we created the simple event-driven workflow that includes EventBus, EventSource and Sensor. I will explain how to set up other kinds of event source and trigger targets in the near future.
Thank you for reading! 🐙


