Use an Amazon S3 trigger in k8s
Invoking AWS lambda functions using the Amazon S3 trigger is a very famous system design pattern on AWS. It can save compute resources and costs. However, once you decide to use k8s as a platform, you may hesitate to use Function as a Service for consistency. So, in this article, I will explains how to use an S3 trigger in k8s with Argo Events.
- Preparation
- Create S3 buckets and a SQS queue and AWS Credentials
- Create a S3 event-driven workflow with Argo Events
- Test the s3 event-driven workflow
- Clean up
- Wrap up
Preparation
Please prepare tools below.
Required
- AWS
- AWS account
- AWS CLI
- Kubernetes
- kubernetes[1]
- Argo Events
- Please refer to my previous post for installing Argo Events.
- Others
- jq
[1] Here is my Kubernetes’s version.
$ minikube profile list
|----------|-----------|---------|--------------|------|---------|---------|-------|--------|
| Profile | VM Driver | Runtime | IP | Port | Version | Status | Nodes | Active |
|----------|-----------|---------|--------------|------|---------|---------|-------|--------|
| minikube | docker | docker | 192.168.49.2 | 8443 | v1.26.3 | Running | 1 | * |
|----------|-----------|---------|--------------|------|---------|---------|-------|--------|
Optional
- Sealed Secrets & kubeseal
- You will store AWS credentials in k8s secrets. If you’d like to manage them in GitOps way, please install Sealed Secrets
- Please refer to my previous post for installing Sealed Secrets.
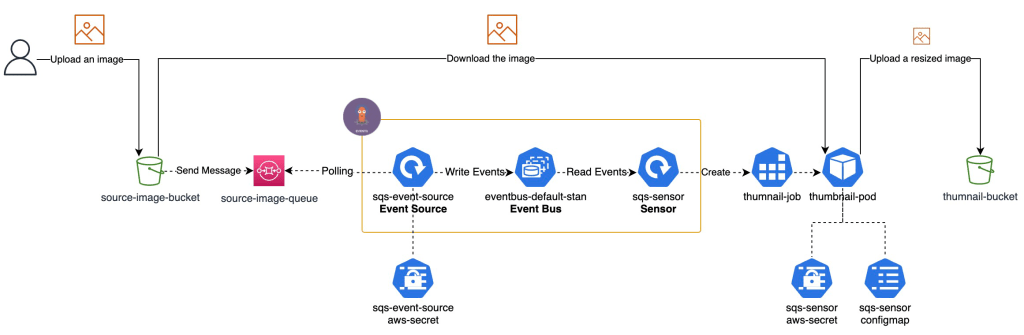
Create S3 buckets and a SQS queue and AWS Credentials
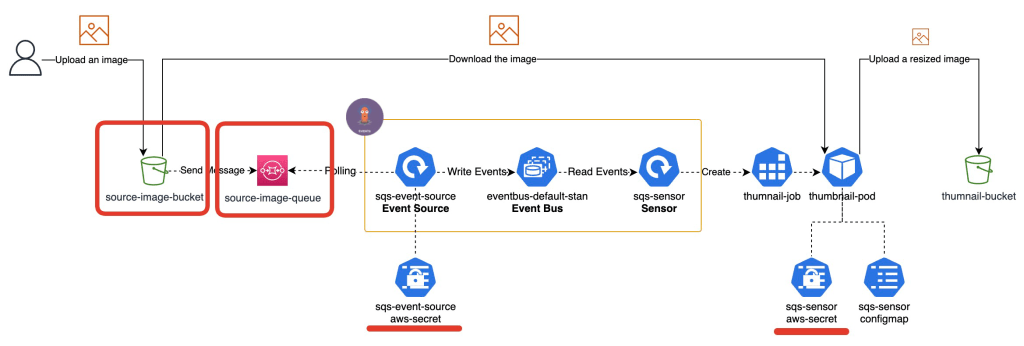
You will create AWS resources with AWS CloudFormation using AWS CLI. So, please configure AWS CLI by following the AWS document so that you can create a stack of CloudFormation using AWS CLI.
Set AWS CLI’s environment variables
To make commands simple, let’s use below AWS CLI’s environment variables. Please make sure your profile can create a CloudFormation stack.
export AWS_PROFILE=YOUR_AWS_ACCOUNT_PROFILE
export AWS_REGION=YOUR_AWS_REGION
Create a stack
Argo Events supports S3 compliant store as the trigger source but does not support AWS S3. So, you will use SQS that is integrated with S3 as a trigger source.
First, please download a CloudFormation template file from my GitHub repository.
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/yukinakanaka/my-manifests/main/argo-events-sqs-lab/aws/aws-cloudformation-template.yaml
Let’s create a stack including S3, SQS and AWS Credentials. This will take a few minutes.
aws cloudformation deploy --template-file aws-cloudformation-template.yaml \
--stack-name s3-trigger-in-k8s \
--parameter-overrides SourceImageBucketName=s3-trigger-in-k8s-$(echo $RANDOM) \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM
Check the stack resources
Please check what resources have been created by the following command.
aws cloudformation describe-stack-resources --stack-name s3-trigger-in-k8s \
| jq '.StackResources[] | { ResourceType: .ResourceType, LogicalResourceId: .LogicalResourceId}'
{
"ResourceType": "AWS::SQS::QueuePolicy",
"LogicalResourceId": "QueuePolicy"
}
{
"ResourceType": "AWS::S3::Bucket",
"LogicalResourceId": "SourceImageBucket"
}
{
"ResourceType": "AWS::SQS::Queue",
"LogicalResourceId": "SourceImageQueue"
}
{
"ResourceType": "AWS::S3::Bucket",
"LogicalResourceId": "ThumbnailBucket"
}
{
"ResourceType": "AWS::IAM::User",
"LogicalResourceId": "UserArgoEventsSensor"
}
{
"ResourceType": "AWS::IAM::AccessKey",
"LogicalResourceId": "UserArgoEventsSensorAccessKey"
}
{
"ResourceType": "AWS::SecretsManager::Secret",
"LogicalResourceId": "UserArgoEventsSensorAccessKeySecret"
}
{
"ResourceType": "AWS::IAM::User",
"LogicalResourceId": "UserArgoEventsSource"
}
{
"ResourceType": "AWS::IAM::AccessKey",
"LogicalResourceId": "UserArgoEventsSourceAccessKey"
}
{
"ResourceType": "AWS::SecretsManager::Secret",
"LogicalResourceId": "UserArgoEventsSourceAccessKeySecret"
}
Create a S3 event-driven workflow with Argo Events
Let’s create a workflow with Argo Events. You can see all manifests of the application in my GitHub repo.
In this application, we will use the SQS queue as an Event Source. When an event happens, the sensor creates a k8s job that downloads a file from the source-image bucket and resizes it, then uploads it to the thumbnail-bucket.
Set AWS CLI’s environment variables
We will use AWS CLI to get AWS resources’ names or values, so please set AWS CLI’s environment variables. Please make sure your profile can read Secret Manager and CloudFormation’s information.
export AWS_PROFILE=YOUR_AWS_ACCOUNT_PROFILE
export AWS_REGION=YOUR_AWS_REGION
Create a namespace
Let’s create a namespace named argo-events-lab.
cat <<EOF > namespace.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: argo-events-sqs-lab
EOF
kubectl apply -f namespace.yaml
Create an Event Bus
EventBus is a Kubernetes Custom Resource which is used for event transmission from EventSources to Sensors. The common practice is to create an EventBus named default in the namespace. So, let’s create it. I chose Jetstream event bus, because it is the latest streaming server implemented by the NATS community.
cat << EOF > event-bus-default.yaml
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: EventBus
metadata:
name: default
namespace: argo-events-sqs-lab
spec:
jetstream:
version: latest
EOF
kubectl apply -f event-bus-default.yaml
Please check the event bus has been created.
kubectl get eventbus.argoproj.io default -n argo-events-sqs-lab
NAME AGE
default 85s
Create an Event Source

First, let’s create a Secret for the AWS credentials to be used by the event source.
Secrets
accesskey=$(aws secretsmanager get-secret-value --secret-id ArgoEventsSource-credentials --query "SecretString" --output text | jq -r .accessKeyId) && \
secretkey=$(aws secretsmanager get-secret-value --secret-id ArgoEventsSource-credentials --query "SecretString" --output text | jq -r .secretAccessKey) && \
kubectl create secret generic sqs-event-source-aws-secret \
--namespace=argo-events-sqs-lab \
--dry-run=client \
--from-literal=accesskey=${accesskey} \
--from-literal=secretkey=${secretkey} \
-o yaml \
> sqs-event-source-aws-secret.yaml && \
kubectl apply -f sqs-event-source-aws-secret.yaml
(Optional) Sealed Secrets
If you prefer Sealed Secrets to Secrets, please use the following command.
accesskey=$(aws secretsmanager get-secret-value --secret-id ArgoEventsSource-credentials --query "SecretString" --output text | jq -r .accessKeyId) && \
secretkey=$(aws secretsmanager get-secret-value --secret-id ArgoEventsSource-credentials --query "SecretString" --output text | jq -r .secretAccessKey) && \
kubectl create secret generic sqs-event-source-aws-secret \
--namespace=argo-events-sqs-lab \
--dry-run=client \
--from-literal=accesskey=${accesskey} \
--from-literal=secretkey=${secretkey} \
-o yaml \
| kubeseal \
--controller-namespace=kube-system \
--format yaml \
> sqs-event-source-aws-secret.yaml && \
kubectl apply -f sqs-event-source-aws-secret.yaml
SQS Event Source
Let’s create an Event Source that type is AWS SQS.
MY_QUEUE_NAME=$(aws cloudformation describe-stacks --stack-name s3-trigger-in-k8s | jq -r '.Stacks[0].Outputs[] | select(.OutputKey=="SourceImageQueue") | .OutputValue') && \
cat <<EOF > sqs-event-source.yaml
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: EventSource
metadata:
name: sqs-event-source
namespace: argo-events-sqs-lab
spec:
sqs:
s3-triggered-queue:
# jsonBody specifies that all event body payload coming from this
# source will be JSON
jsonBody: true
# accessKey contains information about K8s secret that stores the access key
accessKey:
# Key within the K8s secret whose corresponding value (must be base64 encoded) is access key
key: accesskey
# Name of the K8s secret that contains the access key
name: sqs-event-source-aws-secret
# secretKey contains information about K8s secret that stores the secret key
secretKey:
# Key within the K8s secret whose corresponding value (must be base64 encoded) is secret key
key: secretkey
# Name of the K8s secret that contains the secret key
name: sqs-event-source-aws-secret
# aws region
region: ap-northeast-1
# name of the queue. The eventsource resolves the url of the queue from the queue name.
queue: ${MY_QUEUE_NAME}
# The duration (in seconds) for which the call waits for a message to arrive in the queue before returning.
# MUST BE > 0 AND <= 20
waitTimeSeconds: 20
EOF
kubectl apply -f sqs-event-source.yaml
Please check the event source has been created.
kubectl get eventsources.argoproj.io sqs-event-source -n argo-events-sqs-lab
NAME AGE
sqs-event-source 61s
Create a Sensor
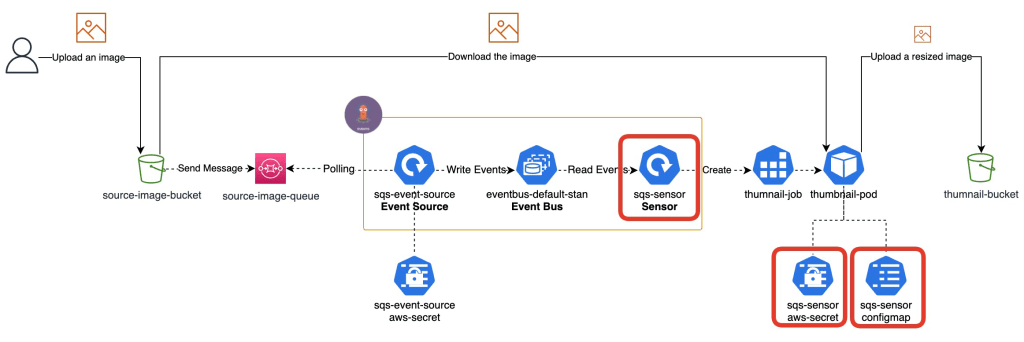
Let’s create a Secret for the AWS credentials to be used by a thumbnail-pod.
Secrets
accesskey=$(aws secretsmanager get-secret-value --secret-id ArgoEventsSensor-credentials --query "SecretString" --output text | jq -r .accessKeyId) && \
secretkey=$(aws secretsmanager get-secret-value --secret-id ArgoEventsSensor-credentials --query "SecretString" --output text | jq -r .secretAccessKey) && \
kubectl create secret generic sqs-sensor-aws-secret \
--namespace=argo-events-sqs-lab \
--dry-run=client \
--from-literal=accesskey=${accesskey} \
--from-literal=secretkey=${secretkey} \
-o yaml \
> sqs-sensor-aws-secret.yaml && \
kubectl apply -f sqs-sensor-aws-secret.yaml
(Optional) Sealed Secrets
If you prefer Sealed Secrets to Secrets, please use the following command.
accesskey=$(aws secretsmanager get-secret-value --secret-id ArgoEventsSensor-credentials --query "SecretString" --output text | jq -r .accessKeyId) && \
secretkey=$(aws secretsmanager get-secret-value --secret-id ArgoEventsSensor-credentials --query "SecretString" --output text | jq -r .secretAccessKey) && \
kubectl create secret generic sqs-sensor-aws-secret \
--namespace=argo-events-sqs-lab \
--dry-run=client \
--from-literal=accesskey=${accesskey} \
--from-literal=secretkey=${secretkey} \
-o yaml \
| kubeseal \
--controller-namespace=kube-system \
--format yaml \
> sqs-sensor-aws-secret.yaml && \
kubectl apply -f sqs-sensor-aws-secret.yaml
ConfigMap
Let’s create a ConfigMap to be used by a thumbnail-pod.
uploadbucket=$(aws cloudformation describe-stacks --stack-name s3-trigger-in-k8s | jq -r '.Stacks[0].Outputs[] | select(.OutputKey=="ThumbnailBucketName") | .OutputValue') && \
kubectl create configmap sqs-sensor-configmap \
--namespace=argo-events-sqs-lab \
--dry-run=client \
--from-literal=uploadbucket=${uploadbucket} \
-o yaml \
> sqs-sensor-configmap.yaml && \
kubectl apply -f sqs-sensor-configmap.yaml
Sensor
Let’s create a Sensor that uses Kubernetes Object Trigger. This time, we will run K8S job that downloads a file from the source-image bucket and resizes it, then uploads it to the thumbnail-bucket. We will use my docker image named yukinakanaka/thumnails. If you’re interested in codes of it, please check my GitHub repository.
*We need to create a ServiceAccount, Role and RoleBindings so that the sensor can create jobs.
cat << EOF > sqs-sensor.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: sqs-sensor-sa
namespace: argo-events-sqs-lab
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: sqs-sensor-role
namespace: argo-events-sqs-lab
rules:
- apiGroups: ["batch", "extensions"]
resources: ["jobs"]
verbs: ["create"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: sqs-sensor-binding
namespace: argo-events-sqs-lab
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: sqs-sensor-role
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: sqs-sensor-sa
namespace: argo-events-sqs-lab
---
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Sensor
metadata:
name: sqs-sensor
namespace: argo-events-sqs-lab
spec:
template:
serviceAccountName: sqs-sensor-sa
dependencies:
- name: sqs-dep
eventSourceName: sqs-event-source
eventName: s3-triggered-queue
triggers:
- template:
name: sqs-job-trigger
k8s:
operation: create
source:
resource:
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
generateName: thumnail-job-
namespace: argo-events-sqs-lab
spec:
ttlSecondsAfterFinished: 120
backoffLimit: 0
template:
spec:
restartPolicy: Never
containers:
- image: yukinakanaka/thumnails:1.0.0
name: thumnail
command:
- python
- app/src/thumnails.py
args:
- "<Bucket: THIS_WILL_BE_REPLACED_BY_PARAMETER>"
- "<ObjectKey: THIS_WILL_BE_REPLACED_BY_PARAMETER>"
env:
- name: AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: sqs-sensor-aws-secret
key: accesskey
- name: AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: sqs-sensor-aws-secret
key: secretkey
- name: UPLOAD_BUCKET
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: sqs-sensor-configmap
key: uploadbucket
parameters:
- src:
dependencyName: sqs-dep
dataKey: body.Records.0.s3.bucket.name
dest: spec.template.spec.containers.0.args.0
- src:
dependencyName: sqs-dep
dataKey: body.Records.0.s3.object.key
dest: spec.template.spec.containers.0.args.1
EOF
kubectl apply -f sqs-sensor.yaml
Please check the sensor has been created.
kubectl get sensors.argoproj.io sqs-sensor -n argo-events-sqs-lab
NAME AGE
sqs-sensor 6m7s
Test the s3 event-driven workflow
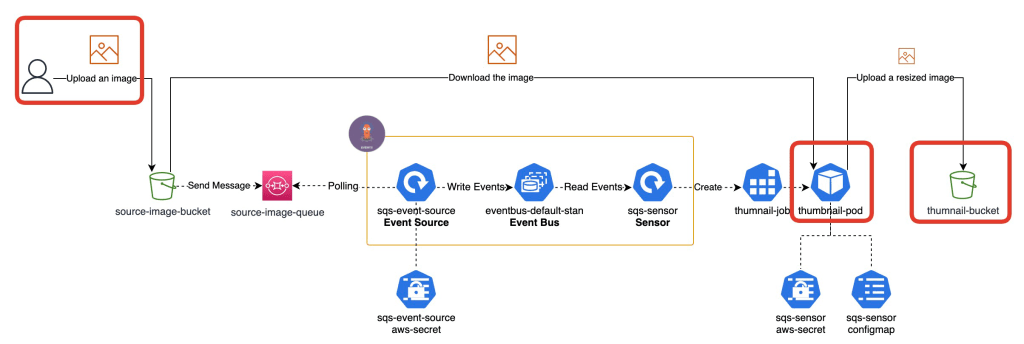
We’re ready to test the s3 event-driven workflow now! So, let’s test it using my blog’s logo.

Set AWS CLI’s environment variables
To make commands simple, let’s use below AWS CLI’s environment variables. Please make sure your profile can read and write objects on S3 buckets and read CloudFormation’s information.
export AWS_PROFILE=YOUR_AWS_ACCOUNT_PROFILE
export AWS_REGION=YOUR_AWS_REGION
Download the image
wget https://yuki-nakamura.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/cropped-img_3457.png \
-O s3-trigger-test.png
Upload the image to your source-image bucket
aws s3 cp s3-trigger-test.png \
s3://$(aws cloudformation describe-stacks --stack-name s3-trigger-in-k8s | jq -r '.Stacks[0].Outputs[] | select(.OutputKey=="SourceImageBucketName") | .OutputValue')
Check a job’s log
Check if pod has been created.
kubectl get pods --no-headers -o custom-columns=":metadata.name" -n argo-events-sqs-lab | grep thumnail-job-
Check log.
kubectl logs \
$(kubectl get pods --no-headers -o custom-columns=":metadata.name" -n argo-events-sqs-lab | grep thumnail-job-) \
-n argo-events-sqs-lab
INPUT:
source_bucket: s3-trigger-in-k8s-32410
source_key: s3-trigger-test.png
upload_bucket: s3-trigger-in-k8s-32410-upload
upload_key: resized-s3-trigger-test.png
Succeeded!
Check the thumbnail image on S3 bucket
aws s3 cp \
s3://$(aws cloudformation describe-stacks --stack-name s3-trigger-in-k8s | jq -r '.Stacks[0].Outputs[] | select(.OutputKey=="ThumbnailBucketName") | .OutputValue')/resized-s3-trigger-test.png \
.
You can see a resized image!

Clean up
Set AWS CLI’s environment variables
To make commands simple, let’s use below AWS CLI’s environment variables. Please make sure your profile can delete objects on S3 and delete CloudFormation stack.
export AWS_PROFILE=YOUR_AWS_ACCOUNT_PROFILE
export AWS_REGION=YOUR_AWS_REGION
Delete objects in S3 buckets
aws s3 rm --recursive \
s3://$(aws cloudformation describe-stacks --stack-name s3-trigger-in-k8s | jq -r '.Stacks[0].Outputs[] | select(.OutputKey=="SourceImageBucketName") | .OutputValue')
aws s3 rm --recursive \
s3://$(aws cloudformation describe-stacks --stack-name s3-trigger-in-k8s | jq -r '.Stacks[0].Outputs[] | select(.OutputKey=="ThumbnailBucketName") | .OutputValue')
Delete the stack
aws cloudformation delete-stack --stack-name s3-trigger-in-k8s
Delete the namespace
kubectl delete namespace argo-events-sqs-lab
Wrap up
We created s3 event-driven workflow in k8s using Argo Events. Let me share my opinion about this architecture’s Pros and Cons.
Pros
- No code for handle SQS’s messages
- Argo Events Source gets messages from a SQS queue and delete them automatically.
- No code for parsing a SQS’s message
- Argo Events has powerful parser and operater
parameters:
- src:
dependencyName: sqs-dep
dataKey: body.Records.0.s3.bucket.name
dest: spec.template.spec.containers.0.args.0
- src:
dependencyName: sqs-dep
dataKey: body.Records.0.s3.object.key
dest: spec.template.spec.containers.0.args.1
Cons
- Job cannot handle multi images at same time because Argo Events can handle only one message per one event.
- Need to store AWS Credentials in k8s Secrets
- If you use EKS and take advantage of IRSA, you don’t have to store them in k8s Secrets.
I’d like to try other tools for event-driven applications such as KEDA and Knative and compare them with ArgoEvents in the future.
Thank you for reading! 🐙

