TL;DR
In this article, I will explain how to get kube-proxy’s metrics via a curl command from a pod via the following command.
curl -s \
http://192.168.64.7:10249/metrics
Monitoring a Kubernetes cluster with Prometheus
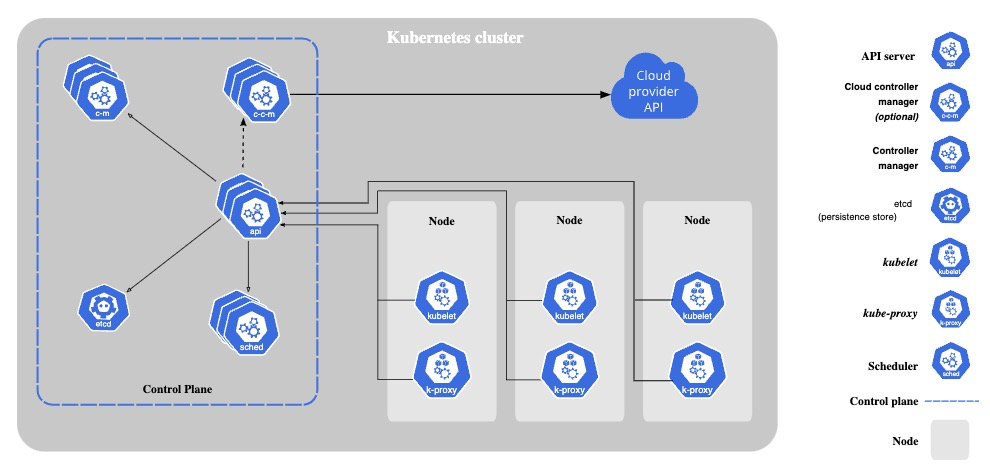
Monitoring a Kubernetes cluster with Prometheus is useful for building dashboards and alerts. However, not many DevOps engineers may understand how Prometheus gets metrics from a Kubernetes Cluster. So let me explain the mechanism!
Kubernetes components emit metrics in Prometheus format via HTTP endpoints, from which Prometheus scrapes metrics.
Example of Kubernetes components that emit metrics:
- kube-apiserver
- kube-scheduler
- kube-controller-manager
- kube-proxy
- kubelet
Preparation
Kubernetes cluster
Please prepare Kubernetes that you can use freely for learning. Here’s my Kubernetes’ version.
kubectl version
Client Version: v1.28.2
Kustomize Version: v5.0.4-0.20230601165947-6ce0bf390ce3
Server Version: v1.28.2
kube-proxy
Before sending requests to proxy, please check its configurations.
bind-address and port
Please check kube-proxy’s bind-address and port.
Example: In my case, bind-address is 0.0.0.0 and port is 10249, 10256. I ran ss command on the master node.
sudo ss -ltp | grep -e kube-proxy -e ^State
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:PortProcess
LISTEN 0 4096 *:10249 *:* users:(("kube-proxy",pid=1469,fd=12))
LISTEN 0 4096 *:10256 *:* users:(("kube-proxy",pid=1469,fd=8))
If bind-address is not 0.0.0.0, kube-proxy is unreachable from outside of host network. So, if you’re bind-address is not 0.0.0.0, please change it.
Change kube-proxy’s bind-address and port via Configmap
I set up my cluster with Kubeadm, then kube-proxy is running as Daemonset and its configuration is defined in ConfigMap.
kubectl get ds kube-proxy -n kube-system
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE NODE SELECTOR AGE
kube-proxy 2 2 2 2 2 kubernetes.io/os=linux 20d
kubectl get fm kube-proxy
NAME DATA AGE
kube-proxy 2 20d
bind-address and port are set in the metricsBindAddress field.
kubectl get cm kube-proxy -o 'go-template={{index .data "config.conf"}}' | yq .metricsBindAddress
0.0.0.0:10249
So, if you need to change it, please edit the field value and restart kube-proxy
Edit Configmap
kubectl edit cm kube-proxy
Restart pods
kubectl rollout restart ds kube-proxy
IP address
Please check your kube-proxy’s ip address. In my case, kube-proxy is running as a pod, so I can check it via kubectl get po -o wide.
kubectl get po -o wide -n kube-system | grep -e kube-proxy -e ^NAME
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
kube-proxy-njzr2 1/1 Running 0 98s 192.168.64.7 k8s-control-plane <none> <none>
Get kube-proxy’s metrics
We will send requests to kube-proxy from a pod.

Create a Pod from which we will send requests
Create a pod that assumes ServiceAccount you just created above.
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: metrics-scraper
namespace: default
spec:
serviceAccount: default
containers:
- command:
- tail
- -f
- /dev/null
image: alpine/curl
name: metrics-scraper
resources: {}
dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst
restartPolicy: Always
EOF
Send requests to kube-proxy
Get a shell of the running pod
kubectl exec -it metrics-scraper -- sh
Send requests to kube-proxy’s metrics endpoints
Let’s get metrics by sending. If you’re interested in each metrics’ meaning, please take a look at the official document.
curl -s \
http://<IP Address>:<Port>/metrics
Example: Total number of iptables rules owned by kube-proxy
/ # curl -s \
http://192.168.64.8:10249/metrics | grep kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_iptables_total
# HELP kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_iptables_total [ALPHA] Total number of iptables rules owned by kube-proxy
# TYPE kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_iptables_total gauge
kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_iptables_total{table="filter"} 3
kubeproxy_sync_proxy_rules_iptables_total{table="nat"} 5
Delete Kubernetes objects
For cleaning up, please delete Kubernetes objects you created in this tutorial.
kubectl delete pod metrics-scraper -n default
Wrap up
We got kube-proxy’s metrics via a curl command from a pod. It should now be clear how Prometheus gets the kube-proxy’s metrics!